Ken ITO & Max YATSUZUKA
 French Finance Minister Bruno Le Maire, right, delivers his speech at the end of the G-7 Finance while Governor of the Bank of France Francois Villeroy de Galhau listens Thursday, July 18, 2019 in Chantilly, north of Paris. Finance ministers from the Group of Seven rich democracies are sounding the alarm on the dangers of cryptocurrencies and pouring cold water on Facebook's Libra as they wrap up a two-day meeting in Chantilly, France. (AP Photo/Michel Euler)(AP/Aflo)
French Finance Minister Bruno Le Maire, right, delivers his speech at the end of the G-7 Finance while Governor of the Bank of France Francois Villeroy de Galhau listens Thursday, July 18, 2019 in Chantilly, north of Paris. Finance ministers from the Group of Seven rich democracies are sounding the alarm on the dangers of cryptocurrencies and pouring cold water on Facebook's Libra as they wrap up a two-day meeting in Chantilly, France. (AP Photo/Michel Euler)(AP/Aflo)
Facebook’s Libra project is currently the center of a controversy in the global financial system.
Shortly after the announcement, we released the previous article relating to the cryptocurrency.
(https://jbpress.ismedia.jp/articles/-/56867)
Since then, remarkable reactions to the project have been expressed all over the world.
This series of articles aims to identify Libra’s shortcomings, then briefly introduce our “Post Blockchain System” plan based on a fundamental condition of neutrality in the financial system by central banks; the NAKASO-IWAI’s neutrality condition.
Firstly, we want to overview some of the reactions to Libra.
 “Libra” can “accelerate” based on the global credit companies’ capabilities.
“Libra” can “accelerate” based on the global credit companies’ capabilities.
1: G7 France Ministers and Central Bank Governors’ Meeting
On 17th and 18th July, the G7 Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors Meeting was held in Chantilly, France. It concluded that Libra, or so-called “stablecoin”, would present “serious risks related to public policy priorities”. (Financial Times https://www.ft.com/content/a6cbf244-a926-11e9-984c-fac8325aaa04)
A “Stablecoin” is a type of cryptocurrency anchored to a reference asset such as a fiat currency or a basket of other stable assets.
Bruno LE MAIRE, the French finance minister, pointed out that “Facebook has hundreds of millions of customers --- a situation that could confer on the proposed coin the attributes of a sovereign currency without the normal rules and controls would come”.
However, he didn’t specify what kind of rule or control is threatened by Libra.
The working group of the G7 led by Benoît CŒURÉ, a French economist from the European Central Bank, set out 4 main recommendations for a “Stablecoin”;
1, Stablecoins should ensure public trust by meeting the highest regulatory standards and being subject to prudent supervision and oversight.
2, Stablecoin initiatives should demonstrate a sound legal basis, in all relevant jurisdictions, to ensure adequate protection and guarantees to all stakeholders and users.
3, They should ensure “operational and cyber resilience”.
4, The management of the assets must be safe and transparent to ensure market integrity.
What draws our attention is the fact that Visa and Mastercard are amongst the members of the “Libra Association”. The global leading and the number 2 lending financial services institutions are supporting the Libra project.
Visa has almost 50% share of the global credit loan market and Mastercard has 26%. The alliance of those big 2 could disseminate this “Stablecoin” rapidly.
2: The BIS General Manager supported a “Central Banks’ Digital Currencies”
Just after the G20 meeting, Augustine CARSTENS, the general manager of the Bank for International Settlement (BIS), told the Financial Times that the BIS supported the efforts of the world’s central banks in creating digital versions of state currencies. (Financial Times https://www.ft.com/content/428a0b20-99b0-11e9-9573-ee5cbb98ed36)
 Facebook “Libra” against “Basel III”
Facebook “Libra” against “Basel III”
The BIS previously held a negative view against cryptocurrencies as they considered them as speculative instruments that cannot be described as money due to the volatility of their value against the most widely used state currencies.
Facebook claimed that “Libra” will be a “stablecoin” with its value backed by a basket of as yet unspecified currencies.
Mr CARSTENS argues that “coins backed by tech giants could “rapidly establish a dominant position” in global finance and pose a potential threat to competition, stability and social welfare”.
“The issue is how will the currency be used?”
He said that ”it might be that it is sooner than we think that there is a market and we need to be able to provide central bank digital currencies.”
As “Basel Ⅰ(1988)“ “Basel Ⅱ(2004)“ and “Basel Ⅲ(2010)“ have clearly shown, the BIS has endeavored to stabilize the global financial system.
Mr. Carlstens also mentioned that “A very simple way to regulate this is to start with anti-money laundering rules“ and “There needs to be evidence for demand for central bank digital currencies.”.
3: Thijs MAAS’ “Foreign Reserve crisis” hypothesis
Mr CARSTENS claims “The issue is how will the currency be used?” Thijs MAAS, a founder and legal consultant at the Law & Blockchain consultancy in Netherland, offers one of the possible answers. He states that Libra can be a threat to the current foreign reserve system (https://hackernoon.com/the-shocking-reason-why-the-united-states-wants-to-stop-libra-5ee97d68647e).
Mr MAAS firstly points to the fact that most of present global reserve currencies are based on the US dollar and governments purchase US long-term bonds, making the assumption that their value will be stable in the future.
 Can Libra replace the US dollar and support the global financial system as a foreign reserve currency?
Can Libra replace the US dollar and support the global financial system as a foreign reserve currency?
He mentions that “The money used to buy Libra is not just retained in a bank. It is also used to buy debt obligations that are issued by states.”.
Currently, many foreign governments hold U.S. Treasuries as a foreign currency reserve. He argues that “This is incredibly important for the U.S., as it helps the government fund its budget. A total of $16 trillion of such U.S. Treasuries is outstanding. This is about 4 times the total amount of cash that’s circulating. And foreign governments hold about 39% of this debt”.
Then he argues that “if Libra is wildly successful, it would get insane bargaining power against governments across the world. It might cause a shift in macroeconomics as we know it“.
“Let’s say Libra would be out to displace the US dollar as the global reserve currency. Libra could potentially negotiate with other governments as follows: “We will buy your debt as collateral for Libra, if you hold Libra as a reserve currency instead of dollars or U.S. Treasuries.””
He argues that the proposal would be appealing to a relatively small government. “They would be assured that
(1) they would be putting their money into something that’s very stable
(2) their money would meanwhile be used to buy their owned debt, which eases their budget and ensures they can lend more money while paying less interest and that
(3) they will not get hurt by (probable) inflation of the US dollar”.
Mr MAAS has concerns that Libra Association may negotiate with a certain country in order to obtain unfair benefits against its competitors. “Note that I am not saying they will do so. I am saying it is a possibility”, he mentions lastly.
In the discussion above, he focused on the US dollar as a “reserve currency”. Indeed, the dollar is virtually the global “Key currency” and Libra could be a great menace to the dollar in each area of the US dollar operations.
Firstly, we point out the risk that in the case where a "stablecoin” replaces the dollar’s position as key currency, global economic growth would be hampered severely.
The long-term interest rate for the US bond can function as an index of growth, but there is no such index in the Libra proposal.
In theory, a stablecoin is a stagnant token for the settlement.
4: Post Blockchain System after NAKASO-IWAI’s condition
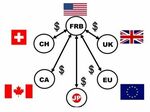
On 15th September in 2008, the bankruptcy filing of Lehman brothers was reported. Hiroshi NAKASO, the then head of the financial market bureau at the Bank of Japan, immediately started to devote himself to establish the “Dollar Swap Network” amongst the 6 major central banks by keeping telephone lines with other central bankers open over 3 days. As a result, the network was successfully established to mitigate any possible secondary damages of the global financial crisis.
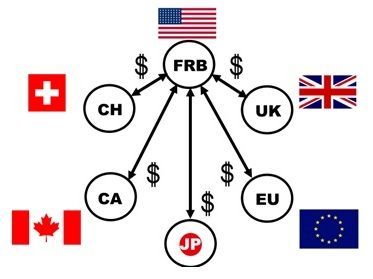
The main purpose of the network was to alleviate the lack of the US dollar supply in the world. The Federal Reserve can create the US dollar as it needs so Hiroshi NAKASO and others from the 6 major central banks decided to establish the US dollar swap network with the Fed to gain a stable access to the US dollar. They endeavored to stabilize the global financial system by utilizing this network.
Katsuhito IWAI, a Japanese economist calls such operations by central banks as a “Big Brother function”. In the novel “1984”, George ORWELL depicts a strict public surveillance by “Big Brother” who is modelled after Joseph STALIN.
A central bank’s surveillance on a market is totally different from the one in “1984” but focusses on stabilizing the financial system without any private profit motivation.
The dollar swap network helped to restore the global financial system and minimize damages. One of the reasons why central bankers successfully established the network in a timely manner is that they acted for the public good rather than for their own interest such as a profit-making motivation.
A basic neutrality is always required in every operation by a central bank.
IWAI predicted that a market without non-profit regulation cannot avoid a breakdown and there is no God’s hand in a free market, which was assumed by the classical political economists. NAKASO had made a huge effort in maintaining a highly neutral position to regularize a rough market and minimize damage.
J. M. KEYNES called an investment without for-profit motive as a “public investment”. Money issuers are requested to have a “public” neutrality in this meaning. We would like to call this “NAKASO-IWAI’s neutrality”.
Most of founding members of the Libra Association are large corporations, such as Facebook, VISA, eBay and Uber. Facebook explained a third-party association established in Switzerland would govern the digital currency system fairly and adequately.
However, these members of the association are commercial enterprises and make management decisions with profit motives. With such private governance, can this association operate neutral monetary policies such that are carried out by central banks, completely independent from a commercial interest?
IWAI also mentioned the research by Anthony ATKINSON and Thomas PICKETTY on economic and social gap, and pointed out that a growth of a digital economy may potentially expand an economic gap. In order to realize fair distribution with real economic growth, highly neutral and non-profit motivated fiscal and monetary policies are crucial.
Can the present Libra plan maintain the global financial stability, independent from for-profit motives?
Since the middle of the 20th century, central banks of each nation have enforced several financial policies in order to stabilize trust in the global financial system. Libra will be backed by a reserve but not systemized to be an asset that has an interest component in order to increase its quantity over time. Any conventional financial policies may not be effective against a new cryptocurrency like Libra. If a cryptocurrency becomes a Key Currency and causes a terrible financial crisis, we will not be surprised at all.
What should we do to prevent such crisis from happening? Our next article aims to propose our “NAKASO-IWAI’s post blockchain system” plan and explain architectures of “EUROR”, “PUBLOR” and other “Post blockchain models“ as a possible solution.
(To be continued.)
Special thanks to Lang WILLETT, Kerryn POOK, and Michelle YATSUZUKA
Dr. Prof. Ken ITO The University of Tokyo
Max YATSUZUKA Associate Member of CPA Australia / The University of Tokyo